Riven
Riven
python logical operators
Logical Operators in Python
Logical operators are used to combine conditional statements. In Python, the three main logical operators are:
- AND
- OR
- NOT
These operators return Boolean values, which can be either True or False. Understanding how to use these operators effectively can greatly enhance your ability to control the flow of your programs.
1. The AND Operator
The AND operator returns True if both operands are true. If either operand is false, it returns False.
Example
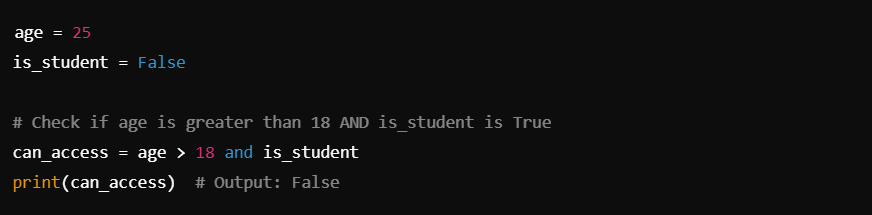
In this example, age > 18 evaluates to True, but is_student is False. Since both conditions must be true for can_access to be True, the overall result is False.
More Complex Example:
You can use AND to evaluate multiple conditions:
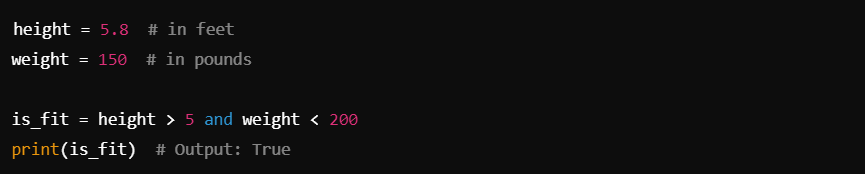
In this case, both conditions (height > 5 and weight < 200) are true, so is_fit evaluates to True.
2. The OR Operator
The OR operator returns True if at least one of the operands is true. It returns False only if both operands are false.
Example
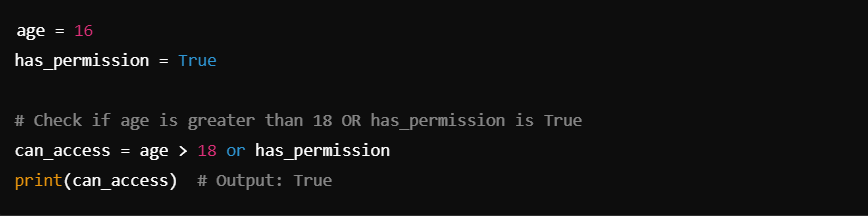
In this case, age > 18 evaluates to False, but has_permission is True. Since at least one condition is true, can_access becomes True.
More Complex Example:
You can combine multiple conditions using OR:

Here, even though has_ticket is False, is_vip is True, leading to can_enter being True.
3. The NOT Operator
The NOT operator is used to invert the Boolean value of an operand. If the operand is True, it returns False, and vice versa

In this example, is_sunny is False, so is_not_sunny becomes True.
Combining Logical Operators:
You can combine these logical operators to create complex conditional expressions:
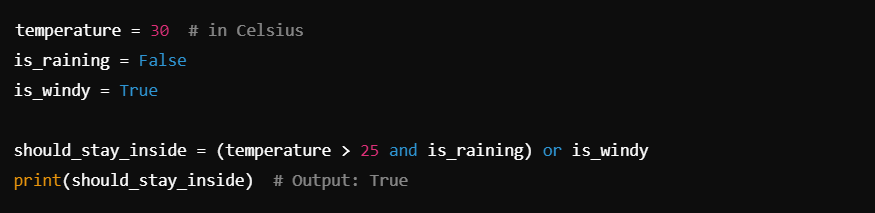
In this example, the expression evaluates to True because even though it’s hot outside, the windy condition makes it necessary to stay inside.