Riven
Riven
Related Article
What is backdoor trojan virus
A Backdoor Trojan is a specific type of malware that provides unauthorized remote access to a user’s system. Unlike traditional Trojans, which may have a variety of functions, Backdoor Trojans are primarily designed to allow an attacker to bypass normal authentication and gain control over the compromised system.
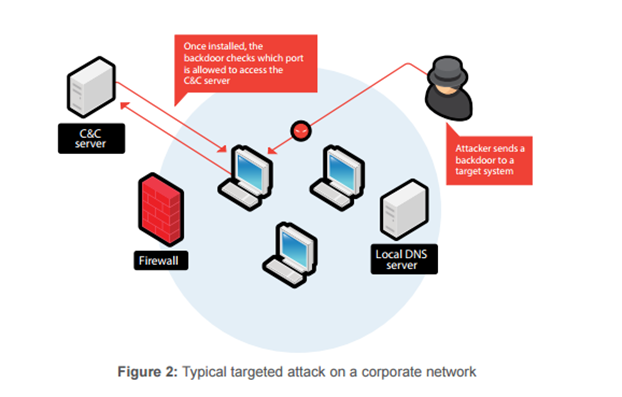
This stealthy intrusion can lead to severe consequences, including data theft, system damage, and the use of the infected machine in further attacks.
The Nature of Backdoor Trojans
The term “backdoor” refers to any method that allows someone to circumvent normal authentication procedures to gain access to a system. Backdoor Trojans hide their presence and often operate undetected, which makes them particularly dangerous. Attackers may utilize Backdoor Trojans to exploit vulnerabilities in a system, which can then be leveraged for various malicious purposes.
How Backdoor Trojans Work
Backdoor Trojans typically operate through a series of steps that include infiltration, control, and exploitation. Here’s a detailed look at the process:
Infiltration:
- Delivery Methods: Backdoor Trojans can be delivered via email attachments, malicious downloads, infected software, or compromised websites. They may also be bundled with legitimate software or disguised as updates.
- Exploitation of Vulnerabilities: Many Backdoor Trojans exploit existing vulnerabilities in the operating system or installed applications. Attackers often scan for weak points in software that can be exploited.
Installation: Once executed, the Backdoor Trojan installs itself on the victim’s machine. This installation process can be silent, meaning the user may not even be aware that the malware has been installed.
Establishing a Connection: After installation, the Trojan opens a communication channel between the compromised machine and the attacker’s server. This connection can use various protocols, including HTTP, FTP, or custom ports.
Remote Access and Control: The attacker can now remotely access the infected system. They can execute commands, steal data, manipulate files, install additional malware, or even use the machine as part of a botnet to conduct further attacks.
Stealth Operations: Many Backdoor Trojans employ techniques to evade detection, such as disguising their processes, altering system files, or using rootkit functionalities to hide their presence from both the user and security software.
Types of Backdoor Trojans
Backdoor Trojans can be categorized based on their functionality and the techniques they employ. Some common types include:
Remote Access Trojans (RATs):
These allow attackers to take complete control of an infected system. They can capture screenshots, log keystrokes, access the webcam, and even control the mouse.
Botnet Trojans:
These connect the infected machine to a network of compromised devices (a botnet) controlled by the attacker. The botnet can be used to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks or spread further malware.
Keyloggers:
While primarily designed to capture keystrokes, some keyloggers function as Backdoor Trojans by sending the captured data back to the attacker and allowing remote control.
File Transfer Trojans:
These Trojans enable attackers to upload or download files to and from the infected system, making it easy to transfer sensitive data or additional malware.
How to Recognize a Backdoor Trojan
Identifying a Backdoor Trojan can be challenging since they often operate stealthily. However, there are several signs that may indicate an infection:
Unusual System Behavior: Slow performance, frequent crashes, or applications that open or close unexpectedly may signal a compromise.
Unauthorized Access: If you notice unfamiliar user accounts, or if files are being accessed or modified without your knowledge, it could indicate unauthorized access.
Increased Network Activity: An unexpected spike in outgoing network traffic can suggest that data is being transmitted from your system to an attacker.
Presence of Unrecognized Applications: If you find applications or processes running on your system that you do not recognize, especially in the Task Manager or System Monitor, it could be a sign of a Backdoor Trojan.
Security Software Alerts: Antivirus and anti-malware software may detect and alert you to the presence of a Backdoor Trojan. Regularly updating this software is crucial for identifying new threats.
How to Prevent Backdoor Trojans
Preventing a Backdoor Trojan infection involves a combination of good practices and the use of effective security measures. Here are some essential strategies:
Use Robust Security Software: Invest in reputable antivirus and anti-malware solutions. Regularly update these programs to protect against the latest threats.
Regular Software Updates: Ensure your operating system and applications are up to date. Software updates often include security patches that close vulnerabilities exploited by malware.
Exercise Caution with Downloads: Avoid downloading software from untrusted sources. Always verify the integrity of software before installation.
Email Precautions: Be wary of email attachments and links, especially from unknown senders. Many Backdoor Trojans are distributed via phishing emails.
Firewall Usage: Enable a firewall on your system to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. This can help block unauthorized access attempts.
Use Strong Passwords: Implement strong, unique passwords for all user accounts and change them regularly. Enable two-factor authentication whenever possible.
Network Security: Secure your home or office network with strong passwords and encryption protocols. Regularly monitor connected devices for any unauthorized access.
Backup Important Data: Maintain regular backups of critical data. In the event of an infection, having a backup ensures you can recover your files without paying a ransom or losing important information.
How to Remove a Backdoor Trojan
If you suspect that your system is infected with a Backdoor Trojan, it’s crucial to act swiftly to mitigate the damage. Here’s a step-by-step guide for removal:
Disconnect from the Internet: Disconnecting from the internet can prevent further data loss and stop the Trojan from communicating with its command and control server.
Boot into Safe Mode: Restart your computer and boot into Safe Mode. This limits the number of processes running, making it easier to identify and remove the malware.
Run Antivirus/Anti-Malware Software: Perform a full system scan with your antivirus or anti-malware software. Follow the instructions for quarantine or removal of detected threats.
Manual Removal: If necessary, manually search for and delete suspicious files and programs. Check the Task Manager for unknown processes and terminate them.
Check Startup Programs: Use tools like the System Configuration utility (msconfig) or Task Manager to disable any suspicious applications from starting with your computer.
Clear Temporary Files: Use system cleanup tools to remove temporary files that may harbor malware remnants.
Review Security Settings: Check and reset firewall and security software settings to ensure they are correctly configured.
Monitor for Future Activity: After removal, keep an eye on your system for any unusual behavior. Continue to run regular scans with your security software.
The Impact of Backdoor Trojans
The impact of a Backdoor Trojan can be severe. Here are some potential consequences:
Data Breaches: Backdoor Trojans can lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data, resulting in data breaches that can affect individuals and organizations alike.
Financial Loss: Compromised systems can lead to financial losses through fraud, theft, or costly remediation efforts.
Loss of Privacy: With remote access, attackers can monitor user activity, leading to a significant invasion of privacy.
Reputation Damage: For businesses, a Backdoor Trojan infection can damage reputation and customer trust, especially if sensitive customer data is compromised.
Legal Consequences: Organizations may face legal repercussions due to data breaches, particularly if they fail to protect customer information adequately.
Case Studies and Examples
Several notable incidents have highlighted the dangers of Backdoor Trojans:
Dark Comet RAT: Dark Comet is a widely used Remote Access Trojan that has been employed in various cybercrime activities. It allows attackers to take control of infected machines and has been used for everything from espionage to data theft.
Back Orifice: Developed in the late 1990s, Back Orifice was one of the first significant Backdoor Trojans. It was designed to provide remote access to Windows systems, exposing numerous vulnerabilities in early operating systems.
Gh0st RAT: Gh0st RAT is a sophisticated Backdoor Trojan often used for espionage. It has been linked to cyber-attacks against various governments and organizations, demonstrating the serious implications of such malware.