Riven
Riven
Python local variable
Local variables are a foundational concept in Python programming, enabling you to manage data within specific contexts, particularly within functions.
What is a Local Variable?
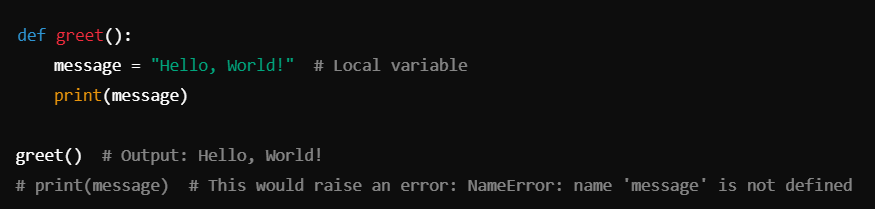
A local variable in Python is a variable that is defined within a function and is only accessible inside that function. Local variables are created when the function is called and are destroyed once the function execution is completed. This encapsulation helps manage data effectively, preventing conflicts with other parts of the program
Example
characteristics of Local Variables
Understanding the characteristics of local variables is essential for effective programming. Here are some key features:
Limited Scope: Local variables can only be accessed within the function where they are defined. They are not visible to other functions or the global scope.
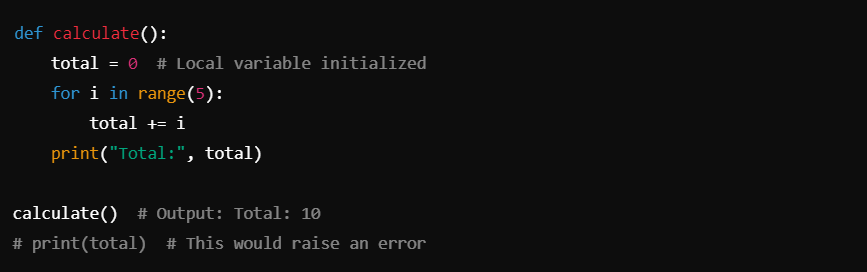
Temporary Lifetime: Local variables exist only during the execution of the function. Once the function completes, the local variable is destroyed.
Dynamic Typing: Python allows local variables to change their type dynamically. You can assign different types of values to the same local variable in subsequent calls.
No Default Value: Local variables must be initialized before use; otherwise, Python will raise a
NameError.
Example
Defining Local Variables
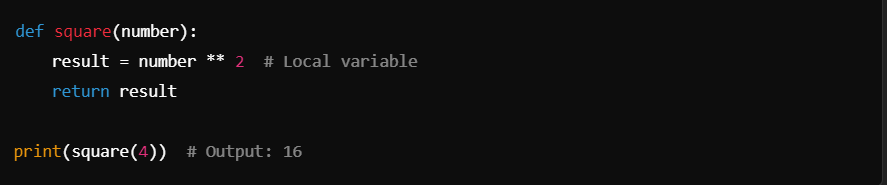
Local variables are defined by simply assigning a value to a name within a function. Here’s the basic syntax:

Example
Scope of Local Variables
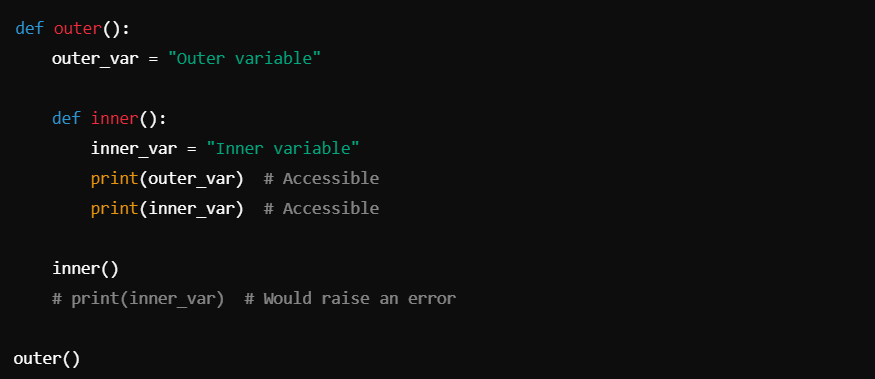
The scope of a local variable refers to the context within which it is defined and can be accessed. Local variables have a local scope, meaning they are only accessible within the function they are declared in.
Example of Scope
Example 1: Basic Local Variable
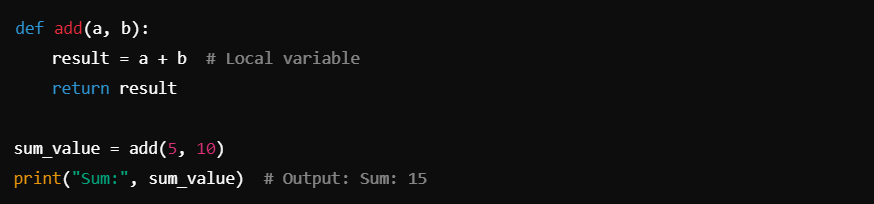
Example 2: Local Variable Initialization

Example 3: Dynamic Typing with Local Variables

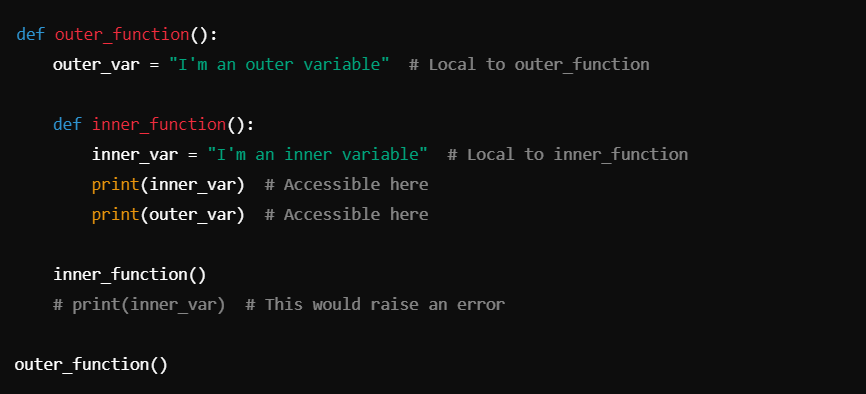
Example 4: Nested Functions and Local Variables